RADIONUCLIDES IN MUSSELS FROM THE EASTERN ADRIATIC COAST, CROATIA –
A CASE STUDY OF THE MEDITERRANEAN MUSSELWATCH PROGRAM
Delko Barišic
1
* and Goran Kniewald
2
1
* Laboratory for Radioecology, Center for Marine and Environmental Research, Rudjer Boškovic Institute,
Zagreb, Croatia - * dbarisic@rudjer.irb.hr
2
Laboratory for Physical Trace Chemistry, Center for Marine and Environmental Research, Rudjer Boškovic Institute,Zagreb, Croatia
Abstract
This communication reports first data from the monitoring of radionuclides in the mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis from croatian coastal
waters, within the scope of the Mediterranean Mussel Watch program. Data from 2 sampling stations are given, from the Šibenik harbour
in the Krka river estuary and from Kaštelabay near the city of Split, where elevated radionuclide activities were expected and found.
Keywords: Mediterranean Mussel Watch, radionuclides, Adriatic Sea
Rapp. Comm. int. Mer Médit., 37,2004
170
Introduction
In 2002 the Commission Internationale pour l’Exploration
Scientifique de la Mer Méditerranée(CIESM) launched a program
called the Mediterranean Mussel Watch(MMW), thereby designing a
regional program for detecting radionuclides and trace contaminants
in “sentinel” organisms (1).
Considering the growing public concern as well as the institutional
enforcement over marine environmental quality, the main objective of
the MMW is to identify spatial and temporal trends through long-term
monitoring at the regional scale. The first phase of the project requires
the identification of existing baseline levels of certain key
radionuclides in Mediterranean coastal waters, measured by the total
body burden of filetr feeder mollusks, preferably Mytilidae. A
comprehensive technical scheme was formulated which focuses on
monitoring strategy (indicator species, sampling sites, sampling
frequencies, selection of calibrated individual organisms), sampling
and treatment of samples, trace level radionuclide measurement, data
management and reporting.
The chosen bio-indicator species is the mussel Mytilus
galloprovincialis, with a geographic distribution recorded on all
coasts of the Mediterranean basin.
The MMW has started with a limited number of sampling sites in
each country. Existing information (and sources thereof) on previous
investigation related to the monitoring of bivalves, other marine
organisms and recent sediments on the eastern Adriatic Coast,
Croatia, have been reported as background information to the project
implementing agency – CIESM (2, 3).
Studies of radionuclides in marine bivalves from croatian waters
have been comparatively few, and little data has been published in
scientific literature. Some recent investigations, dealing with the
distribution of radionuclides between mussels and associated
sediments showed the following activities for some radionuclides in
mussel tissue (wet weight) collected from several sites on Adriatic
coast including the location where ?y and bottom ash (residual after
coal burning) was deposited:
40
K = 94-105 Bq/kg,
232
Th = 0.9-2.3
Bq/kg,
137
Cs = bdl - 1.2 Bq/kg,
238
U = 3-20 Bq/kg (unpublished
internal data of Laboratory for radioecology).
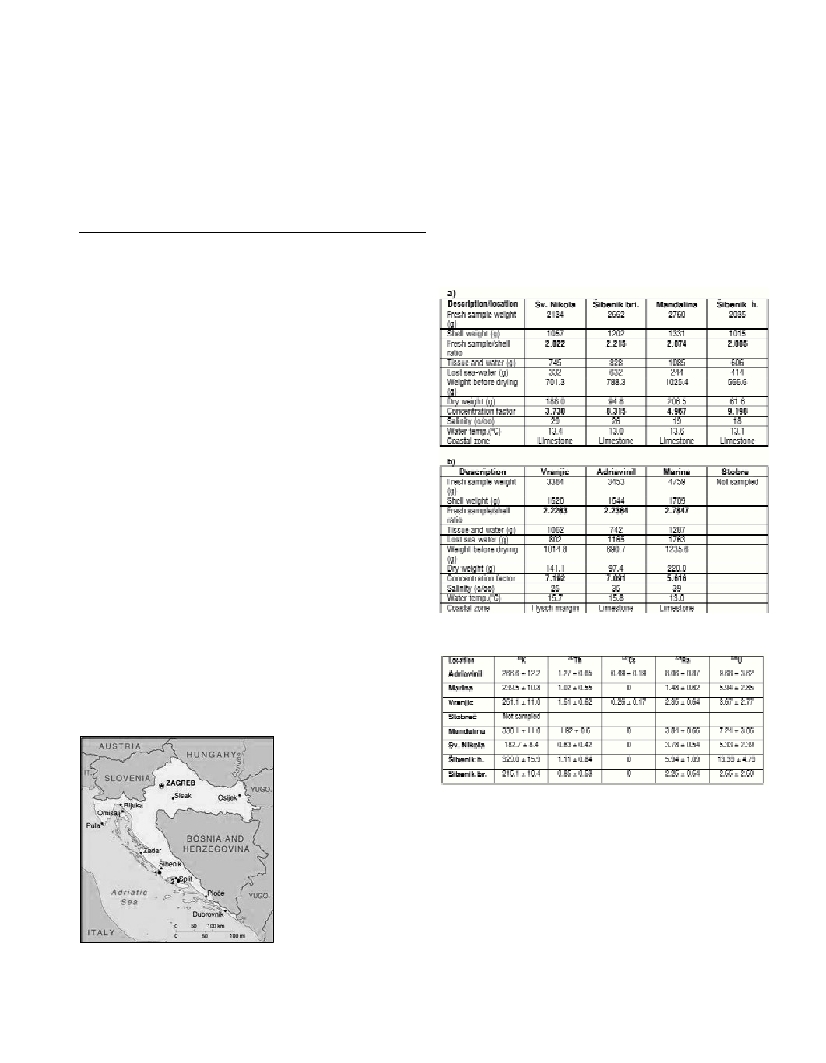
Sampling sites
For specific purposes of
radionuclide monitoring in
the mussel Mytilus gallo-
provincialis on the Croa-
tian coast, two sampling
stations were established
where the identification of
possibly elevated radionu-
clide concentrations due to
specific activities might be
expected. Station 1
(Fig.1) is in the harbour of
the city of Šibenik in the
Krka river estuary. Station
2 (Fig. 1) is in Kaštela bay,
north-east of the city of Split. Samples were taken in April 2003.
Results
Table 1. gives data on mussels and the sampling environment.
Radionuclide activities are given in Table 2.
Table 2. Radionuclide activity (Bq/kg dry weight) in shells tissue
Acknowledgements. The authors thank the Ministry of Science
and Technology of the Republic of Croatia for financial support of
partial studies which have resulted in the present communication.
Authors also thank CIESM for inviting the Center for Marine and
Environmental Research of the Rudjer Boskovic Institute, Zagreb,
Croatia, to join the efforts of the MMW project.
References
1-CIESM, 2002. Mediterranean Mussel Watch – designing a regional
program for detecting radionuclides and trace-contaminants. Briand, F.
(ed.) CIESM Workshop Series No. 15, 136 pages, Monaco.
2-Kniewald, G., and Barišic, D., 2002. Investigations related to the
monitoring of bivalves and other marine organisms on the Eastern Adriatic
Coast (Croatia). Pp. 77-78. In:Briand, F. (ed.) CIESM Workshop Series
No. 15, 136 pages, Monaco.
3-Barišic, D., Vertacnik, A., Lulic, S., Mihelcic, G., Sondi, I, Juracic, M.,
Prohic, E. and Crmaric, R., 1998. Natural radionuclides in recent marine
sediments of the Adriatic Sea. Rapp. Comm. int. Mer Médit. 35: 228-229.
Table 1. a. Data on mussels and the sampling environment (Station 1 –
Sibenik with sublocations). b. Data on mussels and the sampling envi-
ronment (Station 2 – Split with sublocations)