NEW ESTIMATION OF THE ATMOSPHERIC
210
PB FLUX TO THE
NORTHWESTERN MEDITERRANEAN SEA
Garcia–Orellana J.
1*
, Sanchez–Cabeza J.A.
1, 2
, Masqué P.
1,2
and Bruach J.M.
1
1
Grup de Física de les Radiacions - Departament de Física, Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona. 08193 Bellaterra, Spain
* Jordi.Garcia@uab.es
2
Institut de Ciència i Tecnologia Ambientals (ICTA), Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona. 08193 Bellaterra, Spain
Abstract
One of the key parameters needed in geochemical models of
210
Pb, a well known radiotracer of particle dynamics in the marine
environment, is its atmospheric ?ux. There is a scarcity of data about this parameter in the Western Mediterranean Sea, especially regarding
long term records. In this work we have evaluated the
210
Pb annual atmospheric ?ux from the analysis of 10 soils collected from coastal
and island areas.
210
Pb ?uxes ranged from 31±3 to 132±11 Bq·m
-2
·
y
-1
with and average of 75 Bq·m
-2
·
y
-1
, and correlate well with mean
annual rainfall.
Keywords: 210Pb, atmospheric ?ux, Western Mediterranean
Rapp. Comm. int. Mer Médit., 37,2004
199
210
Pb (T
1/2
=22.3 y) is one of the most widely used radiotracers to
study biogeochemical processes in the oceans. One of the parameters
that intervene to constrain the
210
Pb cycle is its atmospheric ?ux. In
the Mediterranean Sea there is a scarcity of data about the
210
Pb
atmospheric ?uxes, especially regarding long term records (1 - 5). The
most common procedure to estimate the annual ?ux is by collection
of wet and dry deposition during long enough time periods to
accommodate seasonal and episodic variations. Other ways are the
use of natural repositories such as snow fields, lake sediments and
soils that integrate large periods of time. In the Western Mediterranean,
the atmospheric
210
Pb ?ux has been estimated in 81.2Bq·m
-2
·y
-1
as
measured in a microbial mat from the Ebro River Delta (558 mm
-1
rainfall) (1), 110 and 102 Bq·m
-2
·y
-1
in Monaco (883mm
-1
) (4, 5),
measuring wet deposition sampled in man-made collectors.
In this work we have evaluated the
210
Pb atmospheric ?ux that has
been deposited over the Mediterranean Sea by determining its
inventory in 10 undisturbed soils from coastal areas and islands,
including Tanger (Morocco); Gata Cape and Minorca (Spain); Frejus,
Port Vendres and Corsica (France); Porto Palo and Camarina (Sicily,
Italy) (Fig. 1). Soils were usually sampled in a land with low
vegetation and without anthropogenic impact. Excess (atmospheric)
210
Pb was determined by the difference of total
210
Pb and
226
Ra
activities. The
210
Pb activity profiles were exponential with depth and
the penetration in soils ranged from 5 cm to 30 cm depending mainly
on the type soil.
210
Pb ?uxes (F) were calculated using F = I·
?
, where
Iis the inventory and
?
is the
210
Pb decay constant (0.0311 a
-1
).
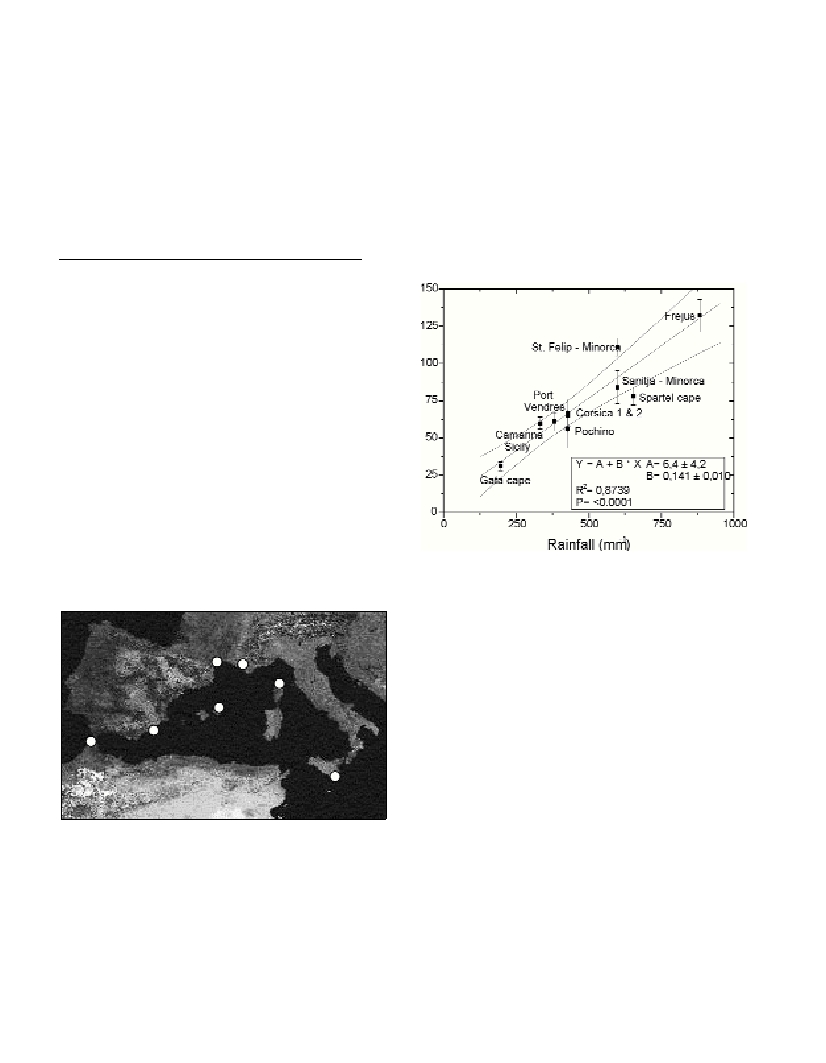
Fig. 1. Distribution of soils collected in this work.
Specific surface activities range from 46 ±3 Bq·kg
-1
in Sanitja
(Minorca) to 102 ±5 Bq·kg
-1
in Port Vendres. Rainfall in the region is
highly variable. For instance, in the North Western Mediterranean
rainfall varies from 428 mm
-1
in Corsica to 883 mm
-1
in Frejus.
210
Pb
?uxes ranged from 31 ±3 to 132 ±11 Bq·m
-2
·
y
-1
with a mean value
of 75 ±27 Bq·m
-2
·
y
-1
and correlated strongly with rainfall (R
2
= 0,87)
(Fig. 2). On the basis of this correlation, we suggest that the
210
Pb
atmospheric ?ux in a given area can be estimated if the mean annual
rainfall is well known at any specific site from the Western
Mediterranean. This facilitates the use of
210
Pb as a tracer of
biogeochemical processes in the Mediterranean Sea and the study of
erosion in soils by using this radiotracer.
Fig. 2. Atmospheric
210
Pb ?uxes vs rainfall in the Western Mediterranean
(y=
210
Pb atmospheric ?ux and x= rainfall).
References
1-Sanchez-Cabeza, J.A., Masqué, P. Martínez – Alonso, M., Mir, J. and
Esteve I., 1999.
210
Pb atmospheric ?ux and rowth rates of a microbial mat
from the Northwestern Mediterranean Sea (Ebro River Delta). Environ.
Sci. Technol.33: 3711-3715.
2-Balkanski, Y.J., Jacob, D.J. and Gardner, G.M., 1993. Transport and
residence times of continental aerosols inferred from global three –
dimensional simulation of
210
Pb. J. Geophys. Res.98: 20573-20586.
3-Preiss, N., Melieres, M.-A. and Pourchet M., 1996. A compilation of
data on lead-210 concentration in surface air and ?uxes at the air – surface
and water – sediment interfaces. J. Geophys. Res.101: 28847-28862.
4-Heyraud, M., 1982. Contribution a l’étude du Po-210 et Pb-210 dans
les organismes marins et luer environment. Pp. 144. In:phD research
work. Université Pierre et Marie Curie, Paris.
5-Tateda, Y., Carvalho, F.P., Fowler, S., Miquel, J.C., 2003. Fractionation
of
210
Po and
210
Pb in coastal waters of the NW Mediterranean continental
margin. Cont. Self Res.23: 295-316.