Rapp. Comm. int. Mer Médit., 37,2004
250
HEAVY METAL AND RADIOACTIVITY IN BIOTA AND SEDIMENT SAMPLES COLLECTED
FROM ÜNYE IN THE EASTERN BLACK SEA
Sayhan Topcuoglu*, Emine Ölmez, Çigdem Kirbasoglu, Y. Ziya Yilmaz, Neslihan Saygin
Çekmece Nuclear Research and Training Center, Istanbul, Turkey- stopcuoglu@superonline.com
Abstract
The heavy metal (Cd, Co, Cr, Cu, Ni, Pb, Zn, Fe and Mn) and radionuclide (
137
Cs,
238
U,
232
Th, and
40
K) concentrations were determined
in macroalgae, mussel, sea snail, fish and sediment samples collected from Ünye region at the eastern Turkish coast of the Black Sea. In
general, as regards the in?uence of the collection site on the whole metal accumulation, Ünye is considered to be more polluted than other
region of the Black Sea. The measured radionuclide concentrations are within the range of the values cited in previous work concerning
the Turkish Black Sea coast.
Key-words: radioactivity, heavy metal, Black Sea
Introduction
The coastal area of Ünye in the eastern Black Sea is nearly 35 km
long. The famous beaches of the Black Sea were located in this area.
Since 2000, nutrients exceeded the algae requirements that caused
eutrophication. In this area, insufficiently treated sewage, municipal
waste combustion and agricultural runoffs are the main sources of the
chemical pollution. At the same time, a fertilizer plant and a coper
smelter located 50 km west of Ünye. Several papers have been pub-
lished concerning heavy metal levels in biota and sediment samples of
Turkish Black Sea coast (1-4). It is well known that many anthro-
pogenic radionuclides entered into the Black Sea after Chernobyl
accident. Nowadays, the anthropogenic radionuclide in the Black Sea
marine environment originated from rivers of the Chernobyl contam-
inated regions and from nuclear power plants in countries around the
Black Sea. Of late, the study of natural radionuclides in the Black Sea
has received increasing attention. Some papers have been published
concerning anthropogenic and natural radionuclides in biota and sed-
iment samples collected from Turkish Black Sea coast (3,5-6).
However, no data on the heavy metal and radioactivity levels of biota
and sediment samples in Ünye area have been published. The objec-
tives of this study are to examine the concentrations of selected heavy
metals (Cd, Co, Cr, Cu, Ni, Pb, Zn, Fe and Mn) and
137
Cs,
238
U,
232
Th and
40
K radionuclides in biota and sediment samples collected
from Ünye coastal area in 2001.
Materials and methods
The macroalgae species (Cystoseira barbata, Ulva lactuca) were
harvested from the sea at low tide. The algae samples were washed in
seawater at the sampling station and transfered to the laboratory. In
the laboratory, they were rinsed in sea water to remove contaminating
materials. Lastly, algae were rinsed in distilled water. Then they were
dried at 85
o
C to constant weight and homogenized. The mussel
(Mytillus galloprovincialis, Venus gallina) and sea snail (Rapan
venosa) and fish (Trahurus trahurus, Sarda sarda, Psetta ssp.) sam-
ples were stored on ice in an insulated box and transferred to the lab-
oratory. Prior to metal analysis, all the soft part and muscle tissue for
each sea snail and all the soft part of each mussel was dissected. The
muscle samples of the fish were prepared from the tail part of the fish.
The samples were pooled and freeze-dried for 10 days to a constant
weight. About 4 cm of the top of sediment samples collected within
the same 3-5 m reach at each sampling site using a Lenz Bottom
Sampler. The collected sediment was sieved in the field and the <63
and <500 µm size fractions were kept for heavy metals anaysis.The
heavy metal concentrations were determined by atomic absorption
spectrophotometer (Varian, Model Spectra AA 100/200). The collect-
ed sediments were sieved and the <500 µm size fraction was kept for
radionuclide analysis. The gamma isotopic analyses were carried out
using a Canberra S-45 4K MCA spectrometer. Other procedures of
the two methods were similar to that previously described (3,6).
Results and discussion
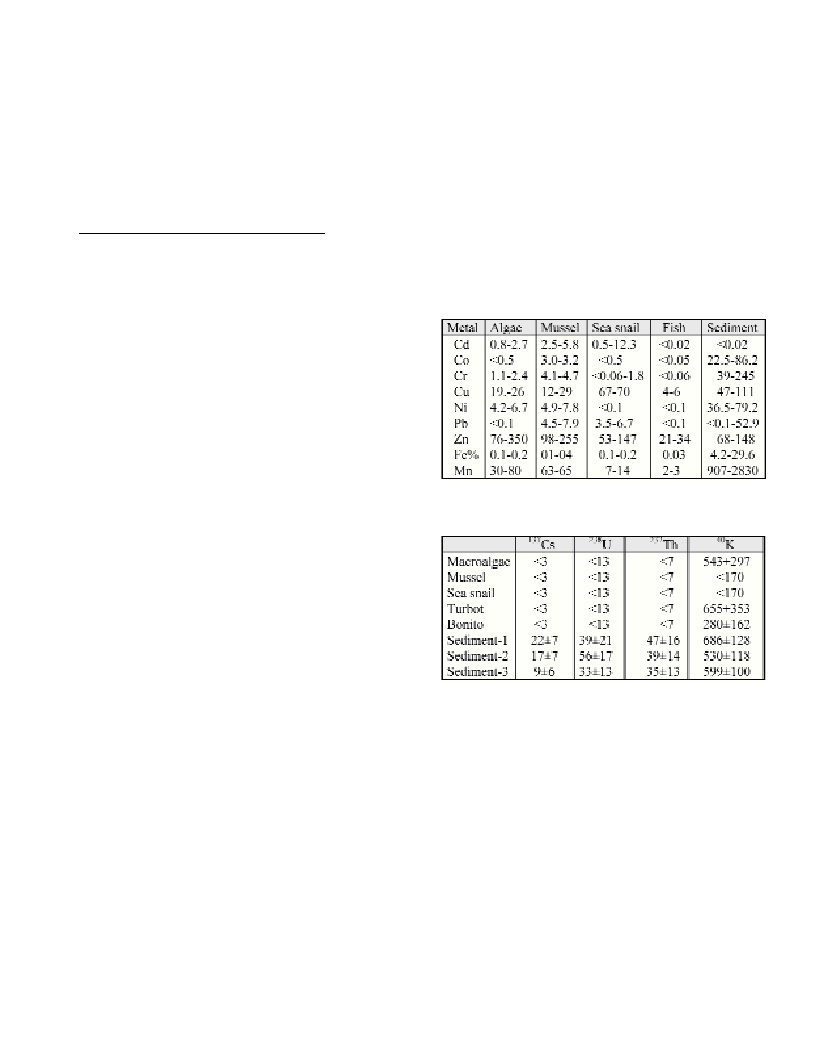
The range of the heavy metal concentrations in biota and sediment
samples are shown in Table 1. In present study, Cu in macroalgae, Pb
in mussel and Zn in sea snail samples are higher than were found in
the same species collected from the other coastal parts of the Black
Sea. At the same time,Co, Cr, Cu, Ni, Pb, Fe and Mn concentrations
in the sediment samples at the present study were higher than other
areas of the Turkish Black Sea coast (3). The radionuclide levels in the
tested biota and sediment samples are shown in Table 2. The
137
Cs
concentrations in the biota samples were found to be below the lower
limit of detection. The
137
Cs and natural radionuclide concentrations
in the sediment samples are lower when compared with the result of
the other parts of the eastern Black Sea (6).
Table 1. The range of the heavy metal concentrations in biota and sedi-
ment samples (µg g
-1
dry weight).
Table 2. Radionuclide concentrations in biota and sediment samples (Bq
kg
-1
dry weight).
References
1-Topcuoglu, S., Güven, K.C., Kirbasoglu, Ç., Ünlü, S., Yilmaz, Y.Z.,
2001. Heavy metals in Marine Algae from Sile in the Black Sea. Bull.
Environ. Contam. Toxicol., 67:288-294.
2-Topcuoglu, S., Kirbasoglu, Ç., Güngör, N., 2002. Heavy metals in
organisms and sediments from Turkish Coast of the Black Sea, 1997-
1998. Environ. Int., 27:521-526.
3-Topcuoglu, S., Ergül, H.A., Baysal, A., Ölmez, E., Kut, D., 2003.
Determination of radionuclide and heavy metal concentrations in biota
and sediment samples from Pazar and Rize stations in the eastern Black
Sea. Fresenius Environ. Bull., 12 (7):695-699.
4-Topcuoglu, S., Güven, K.C., Balkis, S., Kirbasoglu, Ç., 2003. Heavy
metal monitoring marine algae from the Turkish Coast of the Black Sea,
1998-2000. Chemosphere, 52:1683-1688.
5-Topcuoglu, S.,2000. Black Sea Ecology, Pollution research in Turkey
of the marine environment. IAEA Bull, .42 (4): 12-14.
6-Topcuoglu, S., Kut, D., Esen, N., Güngör, N., Ölmez (Egilli), E.,
Kirbasoglu, Ç., 2001.
137
Cs in biota and sediment samples from Turkish
coast of the Black Sea, 1997-1998. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem,.250 (2):
381-384.