FIRST RECORD OF BATHYPOLYPOUS SPONSALIS(CEPHALOPODA: OCTOPODIDAE)
IN THE IONIAN SEA
E. Lefkaditou*, A. Siapatis, A. Chilari, G. Christidis and G. Petrakis
National Centre for Marine Research, Aghios Kosmas, Helliniko, Athens, Greece - * teuthis@ncmr.gr
Abstract
The occurrence of Bathypolypous sponsalis (P. Fischer & H. Fischer, 1892) off the western coast of Peloponnesos is reported. Four
specimens were collected in September 2003 during experimental trawl fishing at 546-655 m of depth. This is the first record of the species
in the Ionian Sea, extending its northern latitudinal distribution in the central Mediterranean.
Key-words : Cephalopods, Ionian Sea
Rapp. Comm. int. Mer Médit., 37,2004
386
Introduction
Bathypolypous sponsalisis the only species of the subfamily
Bathypolypodinae in the Mediterranean Sea, first recorded by Wirtz in
1954 (1). Its origin is considered Lusitanian (2) and further records in
the Mediterranean Seahave been reported mainly for the western part
(3-11) up to the strait of Sicily (12,13). In the eastern Mediterranean
B. sponsalis has been reported only from the Aegean Sea (14, 15, 16).
The species has not been cited previously either in the Ionian or in the
Adriatic Sea.
Materials and methods
The present specimens were collected during a mission carried out
in September 2003 in the southeastern Ionian Sea, for a study of trawl
selectivity in the framework of the project “Development of an
Integrated Management System to support the sustainability of Greek
Fisheries resources (IMAS-Fish)”. Two professional trawlers
equipped with bottom trawl-nets with cod ends of 20 and 40 mm
stretched mesh size, were used. Hauls lasting from 60 to 180 minutes
were performed at a total of 39 sampling stations and depth ranging
from 31 to 650 m. The species was identified following the keys in
Mangold and Boletzky (17). The ventral mantle length (VML) and the
total weight (TW) of individuals per haul were recorded on board.
Results and discussion
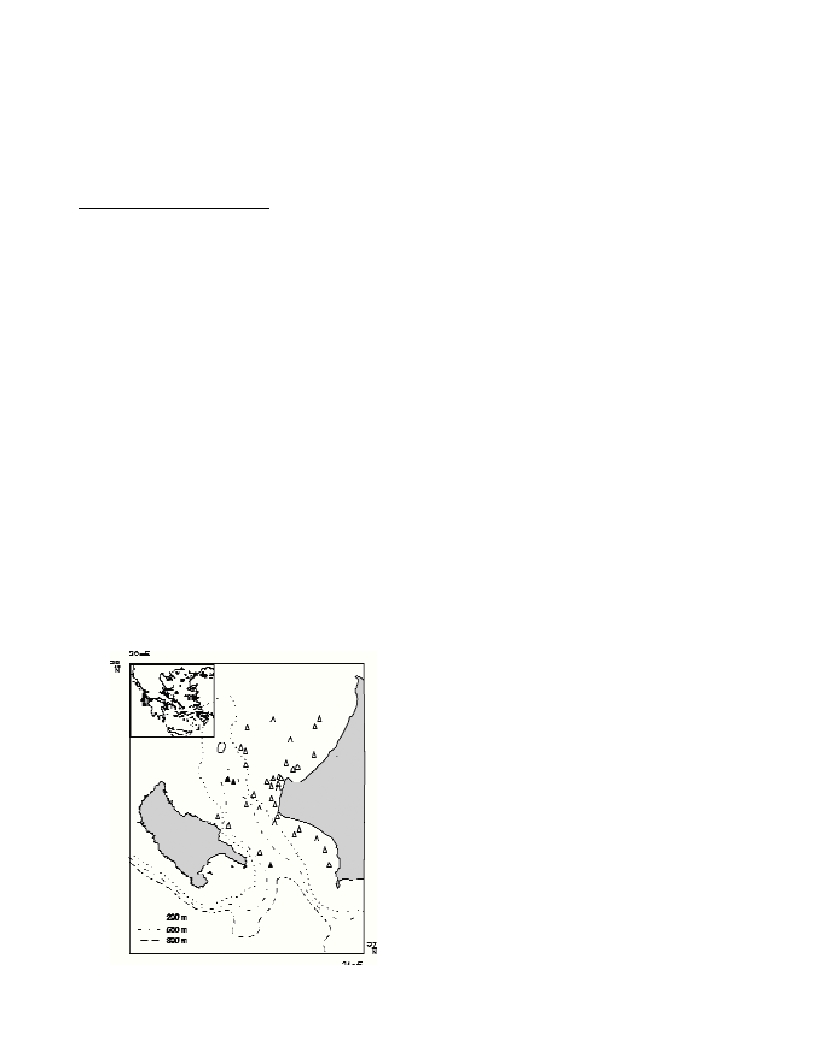
B. sponsaliswas caught during three hauls carried out at depths
between 546 and 655 m (Fig. 1). Four specimens were collected, two
(46 and 55 mm VML, 45 and 35 g TW) by 20 mm and two (42-50 mm
VML, 85 g TW) by 40 mm cod end mesh size. This is the first finding
of the species in the Ionian Sea although several trawl surveys have
been conducted on the slope of the eastern and western Ionian Sea
during the last years (18,19). The closest areas where the species has
been recorded are the Strait of Sicily and the slope off the eastern
coasts of Peloponnesos. B. sponsalis is considered a bathy-benthic
species of eastern Atlantic affinity, extending from 120 m11 to 1835m
of depth but relatively more common between 400-700 m. The large
size of female’s oocytes indicate birth of rather large benthic
hatchlingsand the lack of any pelagic phase in its life-cycle which is
limiting factor for the species dispersal. Thus, the present finding
could be most probably due to the species migration from the southern
Aegean slope around Peloponnesos coastline than to eastward migra-
tion from the slope off southern Sicily. Deep-water mass circulation
due to the gyre activity in this region (20) could probably favor the
suspected migration pattern by creating suitable temperature condi-
tions, which are generally regulating cephalopod species distribution.
References
1-Wirtz K.,1954. Bathypolypous sponsalis (P. et H. Fischer), Céphalo-
pode nouveau pour la Méditerranée. Vie Milieu, suppl., 3: 139-154.
2-Bello G., 1996. Biodiversity of Mediterranean benthic cephalopods.
Biol. Mar. Medit., 3(1): 88-93.
3-Mangold-Wirtz K., 1973. Les Céphalopodes récoltés en Méditerranée
par le “Jean-Charcot” campagnes Polymede I et II. Rev. Trav. Inst. Peches
marit., 37 (3): 391-395.
4-Mangold-Wirtz K., 1963. Biologie des Céphalopodes benthiques et
nectoniques de la Mer Catalane. Vie Milieu, Supl. 13 : 285 p.
5-Sanchez P., 1986. Distribución batimétrica y abundancia de algunos
cefalopódos del mar Catalán. Invest. Pesq.,50(2): 237-246.
6-Villanueva, R., 1992. Deep-sea cephalopods of the north-western
Mediterranean: inclination of up-slope ontogenetic migration in two
bathybenthic species. J. Zool. Lond., 227: 267-276.
7-Quetglas A., Carbonell A., Sanchez P., 2000. Demersal Continental
Shelf and Upper Slope Cephalopod Assemblages from the Balearic Sea
(North-Western Mediterranean). Biological Aspects of Some Deep-Sea
Species. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci,.50 (6): 739-749.
8-Rossi L., 1958. Contributo allo studio della fauna di profondità vivente
presso la Riviera Ligure di Levante. Doriana. Ann. Mus. Civ. Storia Nat.
Genova, suppl., 2(92): 1-13.
9-Tortonese E., 1962. Recenti ricerche sul benthos in ambienti litorali del
mar Ligure. Publ. Staz. Zool. Napoli suppl.,32: 99-115.
10-Lumare F., 1970. Nota sulla distribuzione di alcuni cefalopodi del
Mar Tirreno. Boll. Pesca Piscic. Idrobiol., 25 (2): 313-344.
11-Mannini P., Volpi C., 1989. Nota sulla presenza e distribuzione di
alcuni Cefalopodi del Tirreno Settentrionale. Oebalia, XV-2: 693-701.
12-Jereb P., Baino R., Ragonese S., Mannini P., 1989. Bathypolylous
sponsalis (P. et H. Fischer, 1892). Nova Thalassia, 10, suppl. I: 513.
13-Jereb P., Ragonese S., 1994. The Mediterranean teuthofauna: Towards
a biogeographical coverage by regional census. II: Strait of Sicily. Boll.
Malacol.,30 (5-9): 161-172.
14-D’Onghia G., Matarrese A., Tursi A., MaioranoP., 1996.
Cephalopods collected by bottom trawling in the North Aegean Sea.
Oebalia, 22: 33-46.
15-Salman A., Katagan T., Benli, H.A., 1997. Bottom trawl teuthofauna
of the Aegean Sea. Arch. Fish. Mar. Res.,45(2): 183-196.
16-Lefkaditou E., Peristeraki P., Bekas P., Tserpes G., Politou C.-Y., G.
Petrakis, in press. Cephalopods distribution in the southern Aegean Sea.
Mediterranean Marine Science.
17-Mangold K., Boletzky S. V.,1987. Céphalopodes. Pp. 633-714. In:
Fischer W., Bauchot M.L., Schneider M.(eds), Fiches d’identification des
espèces pour les besoins de la pêche. (Revision 1) Méditerranée et mer
Noire. Vol. I. FAO, Rome,
18-Maiorano P., Mastrototaro F. Casamassima F., Panetta P.,1999.
Comparative analysis of teurthofauna caught b two different trawl nets.
Biol. Mar. Medit., 6(1): 579-583.
19-Lefkaditou E., Maiorano P., D’Onghia G., Mytilineou Ch., in press.
Cephalopod species captured by deep-water exploratory trawling in the
north-eastern Ionian Sea. J. Northw. Atl. Fish. Sci.
20-Theocharis A., Georgopoulos D., Lascaratos A., Nittis K., 1993.
Water masses and circulation in the central region of the Eastern
Mediterranean. Deep-Sea Res.II,40(6): 1121-1142.
Fig. 1. Map of the southeastern Ionian Sea showing the locations of the
hauls performed (white triangles), as well as, of the hauls where
B. ponsaliswas caught.