Rapp. Comm. int. Mer Médit., 36,2001
28
Within the frame of the European Community supported G
EOWARN
(Geo-spatial warning system Nisyros volcano (Greece). An emergen-
cy case study) investigation of the volcanic area of Nisyros active and
passive seismic and seismicity studies have been performed during the
last two years. Our aim is to map the crustal and velocity structure of
this volcanic area and to map the microseismicity in order to delineate
the active fault systems. This project was initiated out of the necessity
to better understand the volcanic behavior of Nisyros. By combining
geodetic, geophysical, geochemical and geological observations it is
intent to correlated magma movements and changes of physical and
chemical parameters of the volcanism. The existence of overheated
(300 C) aquifers at shallow depth (1500 m) below the volcano cause a
permanent danger for the inhabitants and tourists who visit this island.
A decrease of the lithostatic pressure triggered by seismic activity
could cause an explosive reaction of the aquifers and distractions of
the island as already occurred in 1871 and 1873 (1). In the active
experiment we involved 40 ocean bottom seismographs and 20 stan-
dalone digital seismic stations and we recorded 7000 shots in 2D and
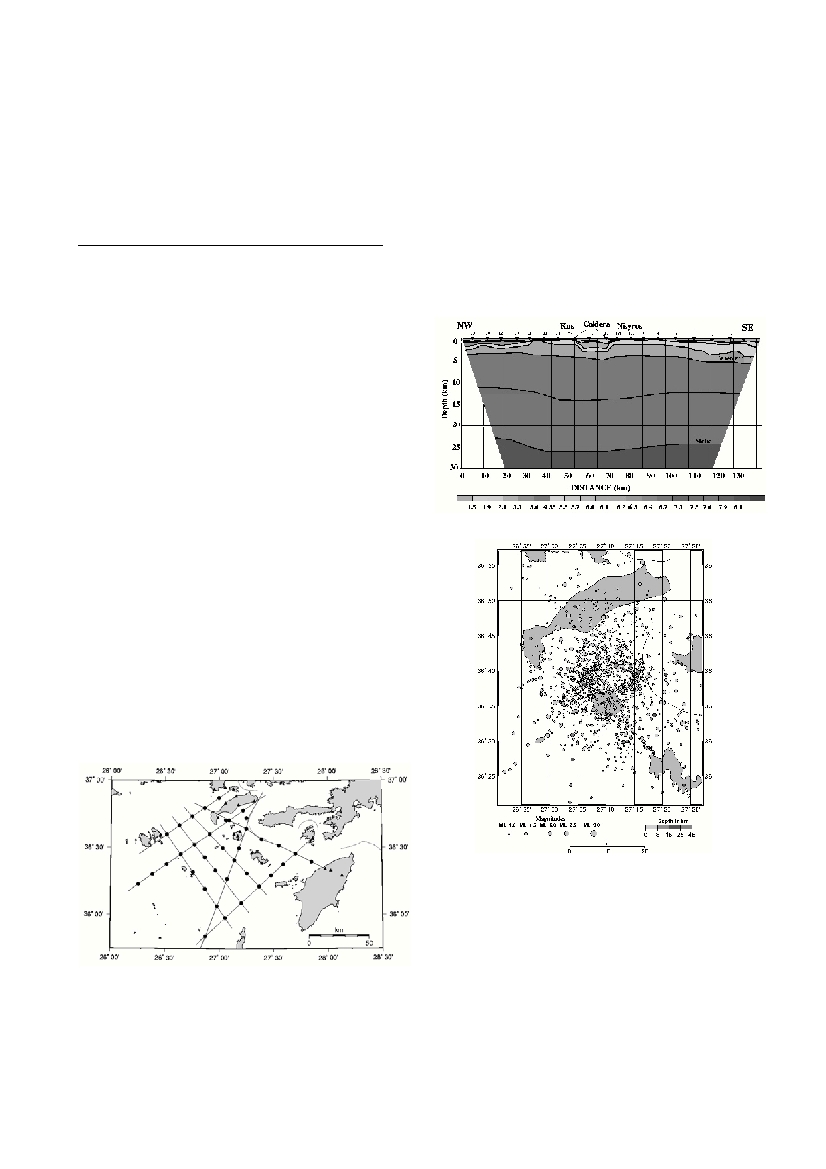
3D geometries (Fig. 1). The evaluation of these data are now in pro-
cess and the crustal structure as is presently known and referred to by
(2) shows that between Rhodes in the south-east and Patmos in north-
west the continental crust of east Aegean sea does not exceed 23 km
in thickness (Fig 2). We could identify through the geometry of the
crust and the distribution of the sediments that the island of Nisyros is
occupied by apophytic intrusion of a much larger volcanic structure
have a caldera of 30 km diameter extending between the southern
coast of Kos and southern coast of Nisyros. By tomographic inversion
of the active seismic observation we could see that the islands of Yali
and Strongili arte also occupied by apophytic intrusions in a similar
fashion as that of Nisyros.
We observed the microseismicity by an on- and offshore seismic
array for 3 mouths in 1997-98 and for 3 month in 2000. The epicentral
d
i
s
t
r
i
butions plotted in Fig.3 delineate the geometry of caldera and it
associated with shallow distribution of foci mainly triggered by
hydrothermal activity and magmatic processes. A series of active fa
u
l
t
s
were identified between the islands of Tilos to Nisyros and between
Nisyros and Yali by the linear distribution of the foci. Other active fa
u
l
t
seems to be east northwest oriented and truncate the caldera at diff
e
r-
ent azimuths. All these active faults can trigger vertical and horizontal
m
ovements and rupture the lithological ove
r
burden thus changing the
p
hysical parameter at depth. We are now in the process of computing
by the active seismic experiment new crustal and tomographic models
of the area and our next step will be to integrate these data to the chem-
ical and geodetic observation the GEOWRN team has collected.
References
1 - Marini, L., Principe C, Ghiodini G, Cioni R., Fytias M., and
MarinelliG., 1993. Hydrothermal eruptions of Nisyros (Dodecanese,
Greece).Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 56: 71-94
2 - Makris, J., T.Chonia, 2000. Active and Passive Seismic Studies of
NisyrosVolcano – East Aegean Sea. In: Communication of the Dublin
institute for advanced studies. Series D, Geophysical Bulletin, 49 : 9-12
CRUSTAL STRUCTURE AND VELOCITY TOMOGRAPHY
OF THE NISYROS VOLCANIC AREA-EAST AEGEAN SEA
Ilinski D.*
1
, Chonia T.
1
, Makris J.
1
, Stavrakakis G.
2
1
Institute of Geophysics, University of Hamburg, Germany - Ilinski@dkrz.de
2
Institute of Geodynamics, National Observatory of Athens, Greece
Abstract:
Within the frame of GEOWARN project active and passive seismic studies have been performed at the volcanic area of Nisyros. Our aim
is to map the crustal and velocity structure of this volcanic area and the microseismicity in order to delineate the active fault systems. In
the active experiment we involved 20 land and 40 bottom seismic stations and recorded 7000 shots in 3D geometry.We identify that the
island of Nisyros is occupied by apophytic intrusion of much larger volcanic structure with a caldera of 30 km diameter extending between
the southern coast of Kos and southern coast of Nisyros.
Keywords: Aegean Sea, crust structure, seismic, volcanology
Figure 1. Locations of OBS (filled circles) and land stations (filled tri-
angles) in Nisyros 2000 tomography project. Black lines are the airgun
shooting profiles.
Figure 2. The P-wave velocity cross-section through Dodecanesos
Figure 3. Microseismic observations in Nisyros area recorded in per-
iods: 1) 11.10.97 – 02.01.98; 2) 15.07.00 – 14.09.00.