Rapp. Comm. int. Mer Médit., 36,2001
122
Metallothioneins are rather small, metal-inducible and metal-binding pro-
teins that are rich in cysteine residues, and are responsible for the metal
d
e
t
o
x
i
fication and metal homeostasis in living organisms [1,2]. Since the
k
n
owledge of the biological functions of MTs, which is based on under-
standing their molecular and physico-chemical properties, is still not com-
plete, our aim was to contribute to this knowledge by characterizing the
metal-binding properties of MT isoforms, induced and isolated from the
d
i
g
e
s
t
ive gland of M. galloprovincialis exposed to cadmium, at a concentra-
tion level close to the cellular one at which metal interacts with the protein.
Experimental
Adult specimens of M. galloprovincialis(5-7 cm, from Lim channel,
Northern Adriatic) were exposed for 14 days to 200 µg Cd dm
-3
(1.8x10
-6
M Cd
2+
added as CdCl
2
) in a continuous ?ow-through seawater system
(S=38‰, 20°C). The biochemical procedure of the isolation and purifica-
tion of MTs from the composite sample of the digestive glands of cadmi-
um-exposedM. galloprovincialisis described elsewhere[
3
,
4
].
For further complexation studies the chromatographic fractions which
contained MT were finally selected based on their highest cadmium con-
tent[
4
,
5
]. MT content was determined according to the Brdicka reaction
[
6
,
7
]
.Amperometric titrations of MTs with cadmium were performed at
constant temperature (25.0±0.5 °C), ionic strength (0.59 M) and pH
(7.9)[
8
].Voltammetric measurements in a differential pulse anodic strip-
ping mode (DPASV) were carried out with a µAutolab instrument (Eco
Chemie, The Netherlands); the measurement parameters are defined else-
where[
8
].
Results and Discussion
Before commencing the amperometric titration, the cadmium[4
]. and
metallothionein[
7
]. content was analysed in the selected chromatographic
fractions (Table 1). It was found that dithiotreitol (DTT), added as a reduc-
ing agent during the MT isolation, competes with MT for Cd
2+
ions and
masks CdMT complex formation[
6
].Therefore, DTT must be removed
from the MT samples. Preferably, in the MT isolation procedure ß-mer-
captoethanol should be used instead.
CdMT complexes[
9
,
1
0
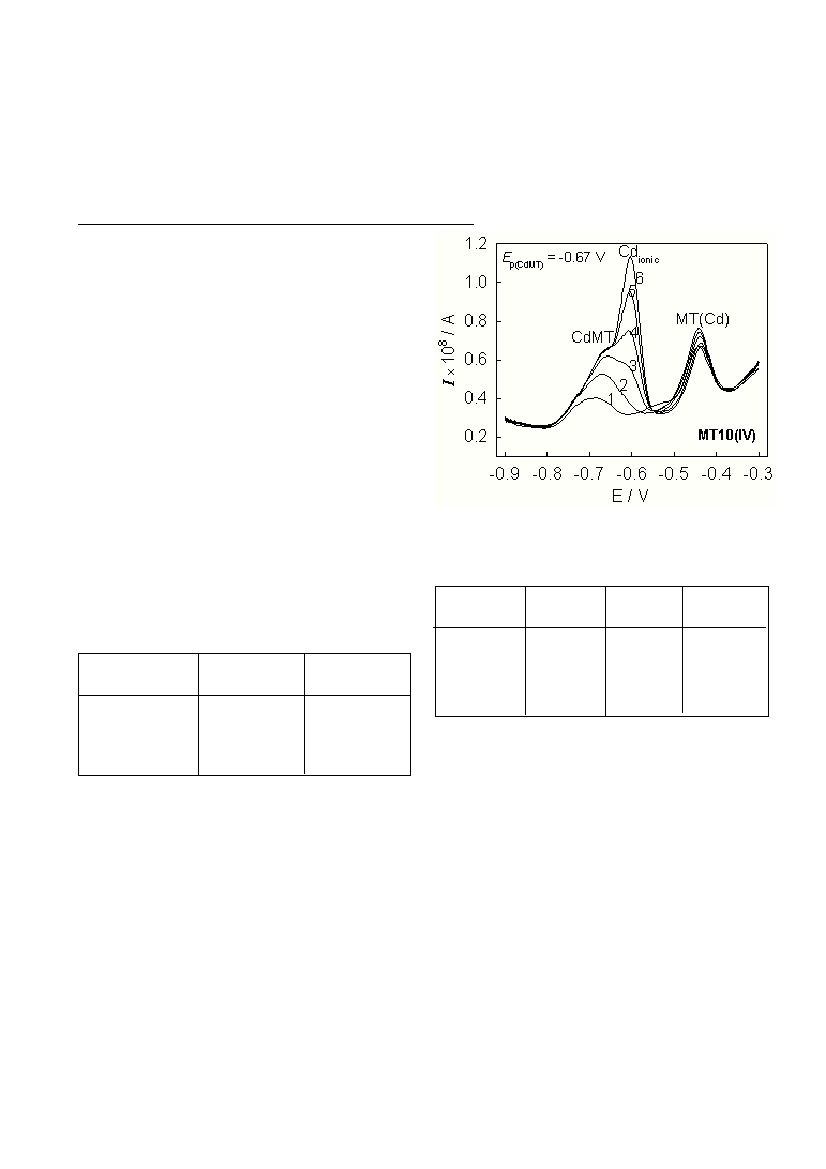
]. give the anodic signal (Fig. 1) with the peak
potential at E
p
˜
-0.66 V.The most positive peak at -0.45 V is assigned to
the oxidation of the mercury electrode in the presence of thiol groups com-
plexed with cadmium[
1
1
]. (Fig. 1). The fact that during the amperometric
titration of MT with CdCl
2
solution two distinct anodic signals, one of the
CdMT complex and the other of Cd
ionic
(E
p
= -0.60 V; Fig. 1), are observed
indicates that under the selected measuring conditions the CdMT complex
is electrochemically inert and a reversible type of complex. From the peak
heights of CdMT and Cd
ionic
signals using the modified van den Berg-
Ruzic-Lee method
6-8
, the complexing capacity (C
L
) (Table 2), and the
apparent stability constants of CdMT were determined. Normalizing the
available MT concentration for complexing cadmium (C
L
) with the total
(analytical) concentration of metallothionein (c(MT)) the number of cad-
mium ions additionally bound by the MT molecule could be determined.
The variations of the Cd
4
and MT
7
concentrations (Table 1) and the stoi-
chiometric ratio (Table 2) in the selected chromatographic fractions, sug-
gest that different purification procedures caused differences in the metal
and MT content of the chromatographic fractions and therefore resulted in
different complexing properties for cadmium.
Acknowledgments.The financial support of the Ministry of Science and
Technology of the Republic of Croatia, projects No. 00981511 and
No.098431, is gratefully acknowledged.
References
1.Binz P.A and Kägi J.H.R., 1999. Metallotionein: Molecular evolution and classification. In:
Klaasen, C.D. (editor) Metallothionein IV. Birkhäuser Verlag, Basel:7-13.
2.Roesijadi G., 1996. Metallotionein and its role in toxic metal regulation. Comp. Biochem.
Physiol., 113C: 117-123.
3.Pavicic J., Skreblin M., Raspor B., Branica M., Tusek-Znidaric M., Kregar I. and Stegnar P.,
1987. Metal pollution assessment of the marine environment by determination of metal-binding
proteins in Mytilus galloprovincialis. Mar. Chem., 22: 235-248.
4.Juric D., 1998. Cadmium-induced synthesis of metallothionein isoforms in the digestive gland
of the mussel Mytilus galloprovinsialis. M.Sc. Thesis, University of Zagreb, pp. 88 (in Croatian).
5.Raspor B., Kozar S., Pavicic J. and Juric D., 1998. Determination of the cadmium and copper
content inherent to metallothionein. Fresenius J.Anal. Chem., 361:197-200.
6.Erk M. and Raspor B., 2000. Advantages and disadvantages of voltammetric method in studying
cadmium-metallothionein interactions. Cell. Mol. Biol., 46: 269-281.
7.Erk M., 2000. Study of chemical reactivity of metallothioneins using electrochemical
techniques. Ph.D.Thesis, University of Zagreb, pp. 107 (in Croatian).
8.Erk M. and Raspor B., 1998. Evaluation of cadmium-metallothionein stability constants based
on voltammetric measurements. Anal. Chim. Acta, 360: 189-194.
9.Raspor B and Pavicic J., 1996. Electrochemical methods for quantification and characterization
of metallotioneins induced in Mytilus galloprovincialis. Fresenius J.Anal. Chem., 354: 529-534.
10.Erk M. and Raspor B., 1999. Electrochemical study on Cd binding to metallotioneins isolated
from the mussel, Mytilus galloprovincialis. J. Electroanal. Chem., 466: 75-81.
11.Mendieta J., Chivot J., Muñoz A. and RodrÌguez A.R., 1995. Electrochemical behavior of
metallothioneins and related molecules. Part I: Lys-Cys-Thr-Cys-Cys-Ala thionein fragment [56-
61] MT I. Electroanalysis,7: 663-669.
PHYSICO-CHEMICAL STUDY OF CADMIUM-METALLOTHIONEIN COMPLEXES ISOLATED FROM
CADMIUM EXPOSED MUSSELS (MYTILUS GALLOPROVINCIALIS)
Marijana Erk*, Dusica Juric, Sonja Kozar, Jasenka Pavicic and Biserka Raspor
Rudjer Boskovic Institute, Center for Marine and Environmental Research, Zagreb, Croatia
Abstract
The amperometric titrations of the purified metallothionein (MT) chromatographic fractions with cadmium ions were performed in the
buffered 0.59 M NaCl solution, pH 7.9 at 25°C. MTs were isolated from digestive glands of the mussels (Mytilus galloprovincialis)
exposed to cadmium. Different purification procedures of the chromatographic fractions could be the reason for the differences in their
metal and MT content. It is perhaps the reason for their different complexing properties for cadmium. The applied differential pulse anodic
stripping voltammetry (DPASV) is suitable for physico-chemical characterization of MTs due to its species-selectivity and sensitivity.
Key words: cadmium, complexation, metallothionein, Mytilus galloprovincialis
Purified
chromatographic
c
(Cd) / M
c
(MT) / M
fractions
MT10(IV)
7.54·10
-8
1.5·10
-6
MT10(V)
5.05·10
-8
3.3·10
-6
MT10(27)
4.34·10
-7
2.1·10
-7
MT20(18)
5.34·10
-7
1.1·10
-7
MT10(12)(13)E.P.
1.08·10
-6
not determined
Purified
chromatographic
c
(MT)* / M
C
L
/ M
C
L
/
c
(MT)
fractions
MT10(IV)
4.0·10
- 9
4.0·10
- 9
1.0
MT10(V)
8.0·10
- 9
1.0·10
-8
1.3
MT10(27)
5.8·10
-10
1.0·10
-9
1.7
MT20(18)
4.3·10
-10
5.7·10
-10
1.3
MT10(12)(13)E.P.1.3·10
- 8
7.0·10
-9
0.5
MT20(17)(18)E.P.4.2·10
- 9
1.4·10
-8
3.3
* aliquot of c(MT) from Table 1 diluted in 20 ml supporting electrolyte
Table 1.Cadmium and MT content in the selected chromatographic frac-
tions
Figure 1 Amperometric titration of MT in 0.59 M NaCl, pH 7.9 with cad-
mium: to 50 µl MT10(IV)(or 4·10
-9
M) Cd
2+
solution is added in the con-
centration range from 1.42·10
-9
M to 8.52·10
-9
M
10
.
Table 2.Cadmium complexing capacity (CL) of MT from differently puri-
fied chromatographic fractions. The results refer to 0.59 M NaCl, pH 7.9