Rapp. Comm. int. Mer Médit., 36,2001
168
Introduction
Küçükçekmece Lake, a lagoon containing brackish water, is located on
the western outskirts of Istanbul . The geographical position of the lake is
41°00' N 28°43' E and it has a 15 km
2
surface area with a maximum
depth of 20 m. Some physical and chemical parameters, measured at dif-
ferent stations in the lake, indicated that Küçükçekmece Lake is eutrophic
(1). Furthermore, some papers have been published previously concerning
heavy metal and radioactivity levels in biota and sediment samples from
the lake (2,3). The collection of sedimenting material in aquatic env
iron-
ments using different types of sediment traps is a method frequently
employed by many scientists for different purposes (4-6). It is well know
n
that studies of vertical particle ?ux have adequately explained the diff
er-
ences with regard to the quantity and quality of the particulate matter
exported from the upper layers as well as seasonal and inter-annual diff
er-
ences (6). A literature rev
iew of various types of sediment traps and brief
survey of applicable sedimentological concepts have been previously pub-
lished by Blomqvist and Hakanson (7).
Our objectives in this study were (a) to measure mass, organic matter
and carbonate ?uxes, (b) variability of ?ux during different seasons under
brackish water conditions and (c) to determine some metal and
210
Po con-
centrations in the sedimenting particulate material.
Materials and methods
Vertical ?ux of particulate mater was determined using a Hydro-Bios
model (Saarso), cylindrical trap with 14 cm diameter and 56 cm height.
The trap had a conical bottom which ended in a 280 ml sample jar.We have
regularly monitored particle ?uxes at one station (12 m depth) in the lake
from September 1998 to July 1999. The depth of deployment was 10 m and
the duration of the deployment was 24 h for each collection. Upon arrival
at the laboratory, sediment trap samples were separated from larger organ-
isms by sieving through 1500 µm and 600 µm mesh sizes, and then the wet
sample was split into 1/4 aliquots using a rotary splitter.Three 1/4 aliquots
were filtered through precombusted and preweighed 47 mm Whatman
polycarbonate filters of 1 µm and 0.2 µm pore size. After that the filters
were rinsed with 250 ml prefiltered distilled water.The filters were than
dried at 60°C for 24 h and weighed. The mass, organic matter and carbon-
ate ?uxes were determined using the methods of Puskaric et al.(4).
Determinations of metal and
210
Po concentrations in the particulate matter
were similar to that previously described (8-9).
Results and discussion
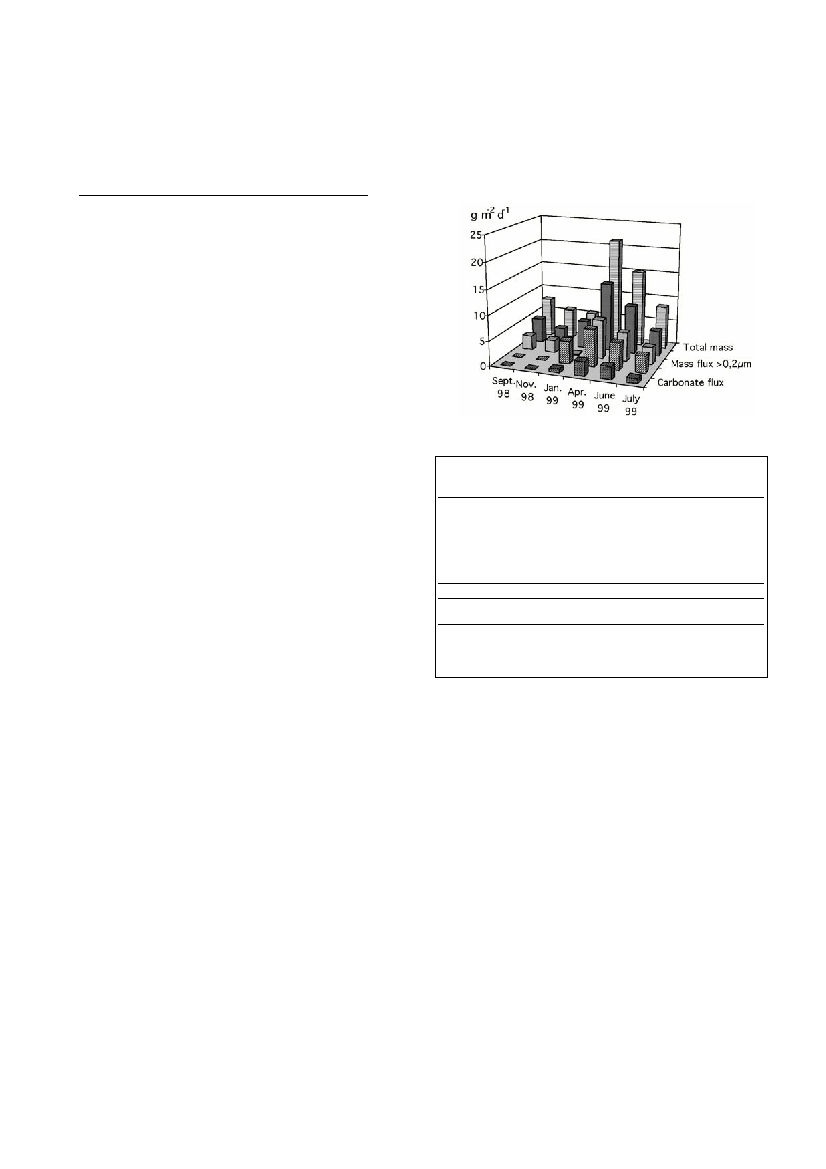
The highest sedimentation ?u
xes of mass, organic matter and carbonate
were recorded in April and June (Fig.1). Our results indicated that these
high ?u
xes were related to phytoplankton and zooplankton abu
ndances.
The Secchi disc depth and suspended matter values in the surface water of
the lake were found to be 0.3 and 0.5 m and 18 and 21 mg l
-1
in April and
July, respectively (1). In contrast, the highest Secchi disc and the lowest sus-
pended matter values were noted in October and December. In the lake
s
surface waters, BOD5 ranged from 0.86 to 9.10 mg l
-1
with the higher va
l-
ues observed in April and July (1). This observation also indicates a rapid
degradation of biogenic materials. Examining the results in detail, it can be
seen that the smallest mass ?ux represented ~40 %, of the total particulate
material with the exception of the January samples. This suggests that nat-
ural planktonic bacteria also play a significant role in the mass ?u
x.
Furthermore, the organic matter ?ux was much greater than carbonate ?u
x
in this brackish water environment. The metal concentrations in sediment
trap water and particulate materials are shown in Table 1. The sediment trap
material (> 1µm) contained a higher concentration of Cr, Sc, Zn and Co than
in the other fractions examined. The Cr, Fe, Zn and Co levels in sediment
trap material (>1 µm) are higher when compared with the deep sediment
samples of Küçükçekmece lake (2-3). The highest
210
Po natural activity in
sedimenting particles from the brackis lake was recorded during May 1998
(1746 Bq kg
-1
in the > 1 µm fraction) (Table 1). Our preliminary results on
vertical particle ?u
xes show that it is necessary to have more ancillary data
(e.g., nitrogen ?ux, lithogenic ?ux, fecal pellet ?ux, chlorophyll a equiva-
lent ?ux) in order to better understand the transfer and transport processes
affecting chemical pollutants and natural radionuclides in this unique brack-
ish lake which is heavily in?uenced by mans activ
ities.
Acknowledgement.Thanks are due to IAEA for supporting part of this study
under its Technical Co-operation project for the Küçükçekmece Lake Reg
ion
(TUR/2/012) and Technical Co-operation project (RER/2/003) for instrumental
asistance . We also thank I.Akkurt for his valuable assistance.
References
1.Topcuoglu S., Güngör N., Kirbasoglu Ç., 1999. Physical and chemical
parameters of brackish water lagoon, Küçükçekmece Lake in Northwestern
Turkey,Toxicol and Environ Chem.69: 101-108.
2. Esen N., Topcuoglu S., Egilli E., Kut D., 1999. Comparison of trace metal
concentrations in sediments and algae samples from the Küçükçekmece
Lagoon and Marmara Sea. J. Radio. Nucl. Chem. 240: 673-676.
3.Topcuoglu S., Kut D., Esen N., Güngör N., Seddigh E., Küçükcezzar
R.,1998.Trace elements and radionuclides in sediments and biota from the
Küçükçekmece Lake. Rapp. Comm. int. Mer Médit, 35: 294-295.
4. Puskaric S., Fowler S., Miquel J-C., 1992. Temporal changes particulate
?ux in the Northern Adriatic Sea. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 32:
267-287.
5. Hansen J.G., Kiorboe T., Alldredge A.L.,1996. Marine snow derived from
abandoned larvacean houses: sinking rates, particle content and mechanisms
of aggregate formation. Mar.Ecol. Prog. Ser.141: 205-215.
6. Andreassen I., Nöthig E-M., Wassmann P., 1996. Vertical particle ?ux on the
shelf off northern Spitsbergen, Norwa
y. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser.137: 215-228.
7. Blomqvist S. and Hakanson L., 1981. A review on sediment traps in aquatic
environments.Arch. Hidrobiol.91: 101-132.
8. Kut D., Topcuoglu S., Esen N., Küçükcezzar R., Güven K.C., 2000. Trace
metals in marine algae and sediment samples from the Bosphorus. Water,Air,
and Soil Poll.118: 27-33.
9.Topcuoglu S., Güngör N., Kirbasoglu Ç., 2001. To establish and compare
for the coastal waters of Turkey.The
210
Po -
210
Pb contents in anchovy fish
and sea snails. IAEA Final Report, Contract No:9712/R1/RO.
VERTICAL PARTICLE FLUX IN A BRACKISH WATER LAGOON, KÜÇÜKÇEKMECE LAKE,
IN NORTHWESTERN TURKEY
S.Topcuoglu*, Ç. Kirbasoglu, D. Kut, N. Güngör, E. Ölmez, N. Esen
Çekmece Nuclear Research and Training Center, Istanbul, Turkey
Abstract
Vertical particle ?u
xes are relatively high in this brackish water region. In the upper 10 m the daily ?ux varied between 5.7 - 21.3; 3.4 4.5
and 0.7 2.9 g m
-2
d
-1
for total mass, organic matter and carbonate, respective
ly. The highest particle ?ux was recorded during April and
June. Concentrations of Zn and
210
Po in sinking particles were found to be 10764 µg g
-1
d.w. and 1746 Bq kg
-1
w.
w. for particles > 1µm.
Key-words: particle ?ux, metal, polonium, brackish water
Fig. 1. Vertical particle ?ux in a brackish lagoon measured over 24h with
Metals µg g-1Sediment trapSedimentSediment
d. w.
water
materialmaterial
June 1998
>1µm
> 0.2 µm
Br
1208±245938±290284±177
Th
0.38±0.187.43±1.153.67±1.41
Cr
15.6±2.5123.4±22.147.4±23.7
Sc
0.41±0.037.73±0.431.09±0.12
Fe
2013±13930019±8624002±845
Zn
3345±22010764±5191868±114
Co
1.09±0.1616.43±1.115.61±1.13
Radionuclide
210
Po Bq kg
-1
w. w.
January 1998
-
587±17
-
May 1998
-
1746±83
983±115
June 1998
-
405±29
491±54
July 1998
-
134±12
Table 1. Metal and 210Po concentrations