Introduction
The tropical algaC. taxifoliawas observed for the first time in the
Adriatic Sea in Starigrad Bay in the summer of 1994. The alga was found
at depths between 0.5 and 20 m, on the hard bottom with photophilic and
sciaphilic biocoenoses and on the sandy and muddy bottoms with seagrass
beds of Posidonia oceanica, Cymodocea nodosaand Zostera noltii(1, 2).
The in?uence of C. taxifoliaon the composition of the Adriatic macro-
zoobenthos hasn’t been researched so far.There are only data about the
in?uence of this alga on the composition of epibionthic meiofauna in the
North Adriatic (3). Its impact on ecological events (4), on invertebrate
composition (5), epiphytic fauna and fish (6) and particularly on the behav-
ior of the sea-urchin Paracentrotus lividus(7, 8, 9) has been researched in
the Mediterranean. In this paper the preliminary data upon macrozooben-
thos composition in the settlements of autochthonous vegetation and set-
tlements attacked by C. taxifoliaand the settlements of C. taxifoliahave
been given.
Material and methods
The investigations were performed by SCUBA diving in Starigrad area
between 2 and 8,8 m depth in the summer of 1998. The material was col-
lected from surface of 1/4 m
2
, in the settlements of autochthonous vegeta-
tion and in the settlements where C. taxifoliaspreads. The samples were
collected: at 2 m depth on the hard bottom in shadow part of inclined (600)
rock where C. taxifoliahasn’t been introduced yet and the part where it has
completely covered the rock; at 5 m depth in the settlement of Cystoseira
adriaticaand in the mixed one with C. taxifolia(approx. 50%); at 3 m
depth on muddy-sandy bottom where the settlement is composed of
Cymodocea nodosaand the mixed one; at 6,6 and 8,8 m depth on sandy-
muddy bottom in the settlement of C. nodosaand the mixed one. All spec-
imens of the dominant groups of macrozoobenthos living in each sample
were sorted, identified and counted.
Results and discussion
The results of the preliminary research indicate that in the sample taken
at 2 m depth on inclined rock (sciaphilic) in the settlement of C. taxifolia
there were more macrozoobenthic species (34 species) than in the settle-
ment of sciaphilic algae (17 species); superior in number are sponges and
molluscs. The number of species at 5 m depth in mixed settlement of C.
adriaticaand C. taxifoliais higher (16 species) than in C. adriaticasettle-
ment (14 species); the number of molluscs was the same in both samples
(7 species); the sponges (3 species) were found only in C. adriaticasettle-
ment, while echinodermata (2 species) were found only in the mixed sam-
ple (Fig. 1).
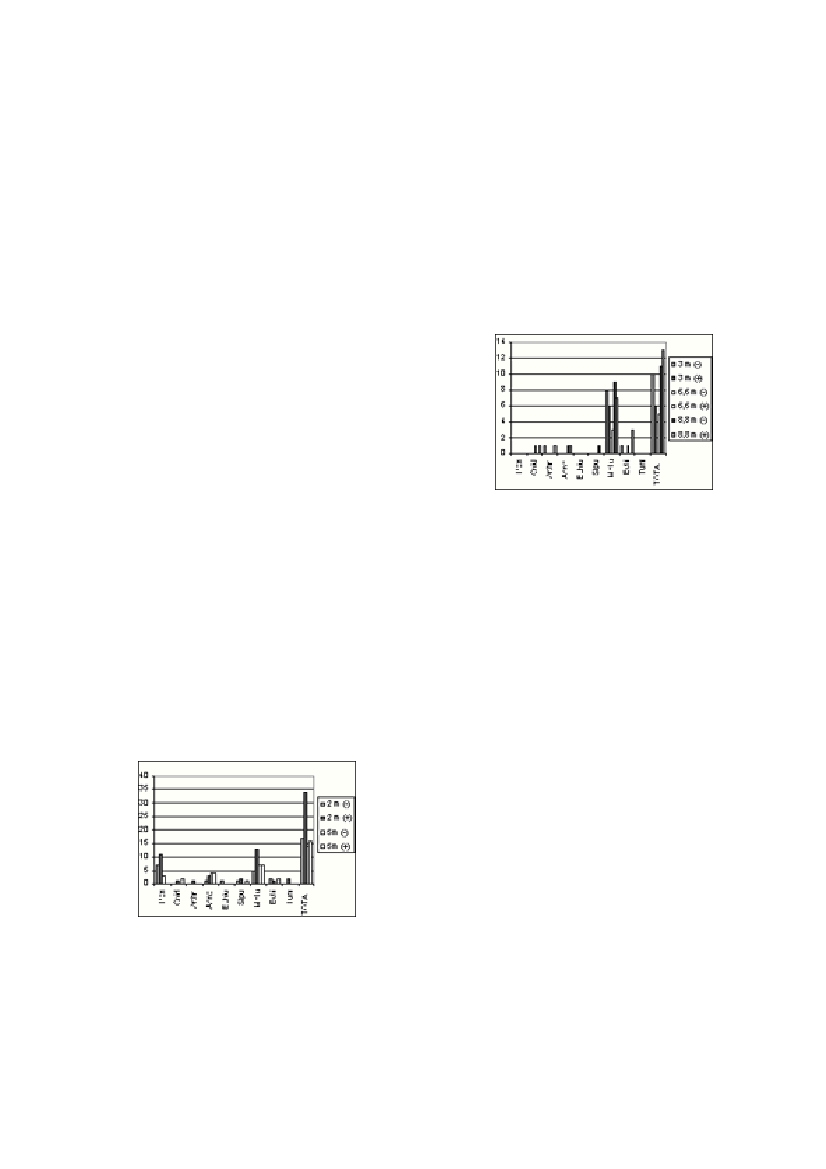
Fig.1. Number of macrozoobenthic species in samples
without (-) and with C. taxifolia(+).
On muddy-sandy bottom (3 m depth) in the sample of C. nodosawe
have recorded more species (10 species) than in the mixed sample (6
species). In both samples the most numerous are molluscs. On sandy-
muddy bottom (6,6 m depth) in the sample of C. nodosathere haven’t been
recorded any macrozoobenthic species, while in the mixed settlements 5
species were recorded. At 8,8 m depth in C. nodosasettlement 11 species
were observed and 13 species in mixed one. In the mixed settlement there
were defined the single species of cnidarians and crustaceans and 3 species
of echinoderms which weren’t recorded in the settlements without C. tax-
ifolia. However, the number of molluscs is higher in C. nodosasettlement
(9 species) than in the mixed one (7 species) (Fig. 2).
Fig. 2. Number of macrozoobenthic species in settlements
without (-) and with C. taxifolia(+).
Analysing the results of the preliminary research the question was
raised: Does the tropical algaC. taxifoliain?uence the macrozoobenthos
composition and to what extent? The final answer should be found in more
complex researches that are in the course.
References
1 - Zuljevic A., Antolic B., Span A. 1998 a. Spread of the introduced tropical
green algaCaulerpa taxifoliain the Starigrad bay (island Hvar, Croatia).
Third Internatonal Workshop on Caulerpa taxifolia. Boudouresque C.F.,
Gravez V., Meinesz A., Palluy F. (eds), GIS Posidonie publ.: 51-59.
2 - Zuljevic A., Antolic B., Span A. 1998 b.The genus Caulerpa (Caulerpales,
Chlorophyta) in the Adriatic. Rapp. Comm. int. Mer Médit., 35: 584-585.
3 - Zavodnik N., Travizi A., Jaklin A., Labura Z. 1998. Caulerpa taxifolia
(Chlorophyta) in the north Adriatic Sea at Malinska (Krk Island, Croatia).
Third Internatonal Workshop on Caulerpa taxifolia. Boudouresque C.F.,
Gravez V., Meinesz A., Palluy F. (eds), GIS Posidonie publ.: 175-184.
4 - Boudouresque C.F., Meinesz A., Ribera M.A., Ballesteros E. 1995. Spread
of the green algaCaulerpa taxifolia(Caulerpales, Chlorophyta) in the
Mediterranean: possible consequences of the major ecological event. Sci. Mar.
(Supl.1): 21-29.
5 - Bellan-Santini D. 1995. Faune d’invertébres du peuplement à Caulerpa
taxifolia. Données préliminaires pour les côtes de Provence (Méditerranée).
Biol. Mar. Medit., 2 (2): 635-643.
6 - Relini G., Relini M., Torchia G. 1998. Fish and epiphytic fauna on
Caulerpa taxifoliaand Cymodocea nodosaat Imperia (Ligurian Sea). Third
Internatonal Workshop on Caulerpa taxifolia Boudouresque C.F., Gravez V.,
Meinesz A., Palluy F. (eds), GIS Posidonie publ.: 185-195.
7 - Ruitton S., Boudouresque C.F. 1994. Impact de Caulerpa taxifoliasur une
population de l’oursin Paracentrotus lividusà Roquebrune-cap Martin
(France). First Internatonal Workshop on Caulerpa taxifolia. Boudouresque
C.F., Meinesz A., Gravez V. (eds), GIS Posidonie publ.: 371-378.
8 - Bellan-Santini D., Arnaud P., Bellan G. 1996. Affinites entre peuplements
Mediterraneens benthiques avec et sans Caulerpa taxifolia. Second
Internatonal Workshop on Caulerpa taxifolia. Ribera M.A., Ballesteros E.,
Boudouresque C.F., Gomez A., Gravez V. (eds) Publicacions Universitat
Barcelona: 387-390.
9 - Lemée R., Boudouresque C.F., Gobert J., Malestroit P., Mari X., Meinesz
A., Menager V., Ruitton S. 1996. Feeding behaviour of Paracentrotus lividus
in the presence ofCaulerpa taxifolia introduced in the Mediterranean Sea.
Oceanol. Acta, 19 (3-4): 245-253.
DOES TROPICAL ALGA CAULERPA TAXIFOLIA(VAHL) C. AGARDH INFLUENCE
THE MACROZOOBENTHOS COMPOSITION ?
Grubelic I.*, Antolic B., Bartulovic M., Zuljevic A. and Simunovic A.
Institute of Oceanography and Fisheries, Split, Croatia - grubelic@izor.hr
Abstract
Relationship between macrozoobenthos species in the autochthonous vegetation settlements and in the settlements infested and prevailed
by tropical algaCaulerpa taxifolia, have been observed in the summer of 1998 (Starigrad Bay, Hvar Island, Adriatic Sea). Preliminary
results indicate that the number of macrozoobenthic species is higher in the samples of autochthonous vegetation with C. taxifoliathan in
the samples without it, which is not in accordance with data from the researches in the Mediterranean, where the negative in?uence of
C.taxifolia to biological diversity was recorded. In order to give precise answers to the question in the title, the research has been carried
on.
Key-words: macrozoobenthos, Caulerpa taxifolia, Adriatic Sea
Rapp. Comm. int. Mer Médit., 36,2001
390