
|
Relevant synonyms Meristic formula |
|
| photo: Daniel Golani |
|
SHORT
DESCRIPTION
size : 4-10 cm (max. 15 cm). |
DISTINGUISHING CHARACTERISTICS Epigonidae – Base of soft ray portion of dorsal, anal and caudal fins covered with scales. BIOLOGY / ECOLOGY
habitat : during the day hides in rocky habitat, while at night preys in open water close to the substrate to depths of 50 m. |
|
1st
MEDITERRANEAN RECORD
|
|
|
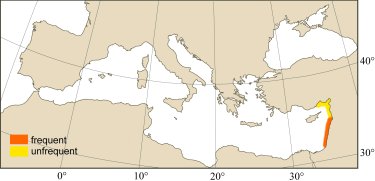
DISTRIBUTION
|
ESTABLISHMENT SUCCESS
|
|
|
MODE OF
INTRODUCTION |
IMPORTANCE TO
HUMANS |
|
KEY REFERENCES
|
|
|
 Apogon smithi
Apogon smithi