
|
Meristic formula D, XI-XII + 9-11; A, III + 7-9; P, 14-15; V, I + 5; LL, 46-56; GR, 20-25 |
|
| photo: Valter Žiža |
|
SHORT
DESCRIPTION
color : body silvery-grey to dusky-green on the back with silvery white belly. Four wide longitudinal blackish to brown stripes on the flank. The 3rd stripe extends to the middle of caudal fin. Both caudal fin lobes with two horizontal stripes, a black spot on the tip of upper lobes. Large black spot between 3rd-7th dorsal spines. Two slightly slanted dark stripes on the posterior part of dorsal fin. Juveniles have 6-7 grey vertical bars. size : 10-15 cm (max. 30 cm). |
DISTINGUISHING CHARACTERISTICS
Other families: lack of two spines on the operculum (three such spines in Serranidae); lack of longitudinal stripes (young specimens of Epinephelus costae have brown longitudinal stripes). BIOLOGY / ECOLOGY
|
|
1st
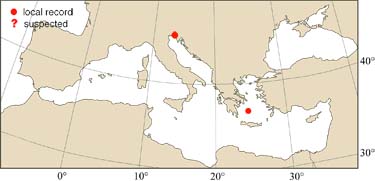
MEDITERRANEAN RECORD
|
|
|
DISTRIBUTION
|
ESTABLISHMENT SUCCESS
|
|
|
MODE OF
INTRODUCTION |
IMPORTANCE TO
HUMANS |
|
KEY REFERENCES
|
|
|